Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: What You Need to Know
UT Health Austin reproductive endocrinologist and infertility specialist Dr. Winifred Mak answers common questions about PCOS
Reviewed by: Winifred Mak, MD, PhD
Written by: Lauryn Feil
Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted directly into the blood where they travel throughout the body, coordinating complex processes like growth, metabolism, and fertility. When your body does not produce the right amount of hormones, conditions may develop that can affect various functions in your body and your overall quality of life.
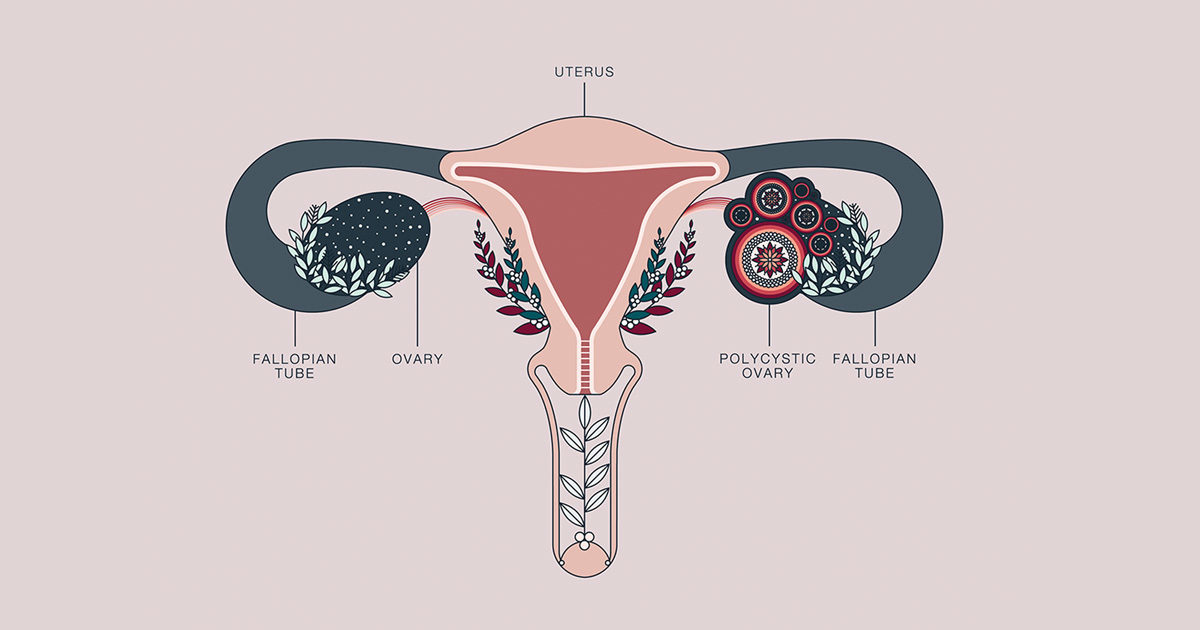
One example of a condition linked to a hormonal imbalance is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), where women produce an excess of male hormones (androgens). PCOS is a common condition, affecting one in ten women of reproductive age (15 – 44 years), but nearly half go undiagnosed. PCOS can lead to female infertility and is a risk factor for diabetes, uterine cancer, and heart disease.
PCOS can be a lifelong disorder that often requires specialized care to manage. Winifred Mak, MD, PhD, a reproductive endocrinologist and infertility specialist who also serves as a part of UT Health Austin’s Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility care team, answers common questions about PCOS symptoms, available treatment options, and more.
What causes it?
Doctors are not entirely sure what causes PCOS, but believe it involves a combination of disorders associated with an excess of androgens and insulin resistance that results in irregular ovulation and periods. The high levels of androgens prevent the ovaries from responding normally to hormones that enable an egg to be ovulated each month. Studies show that PCOS runs in families and is likely caused by many genes.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms include irregular menstrual cycles, excess facial and body hair, male pattern baldness, severe acne, dark skin patches in the groins/armpits/body creases, an abundance of small cysts (fluid-filled sacs) on one or both ovaries, anxiety, depression, difficulty in losing weight, or weight gain.
How does it affect the body?
Because PCOS affects ovulation, women with this condition may have a difficult time getting pregnant. In addition to infertility, approximately half of people with PCOS experience weight gain or obesity that is difficult to manage. PCOS, along with obesity, can increase your risk of heart disease as well as becoming prediabetic or diabetic. Having fewer than four periods a year can also lead to abnormal thickening of your uterine lining and increase your risk of developing endometrial cancer.
How is it treated?
There, unfortunately, is no cure for PCOS, but treatment focuses on managing and slowing the progression of symptoms to lower your risk of long-term health problems. One of the best treatments for PCOS is a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a low glycemic index diet, which means eating foods with complex carbohydrates. Losing weight can help with all symptoms associated with PCOS; however, some women may need medication to help improve insulin resistance and slow prediabetic or diabetic progression.
Other treatments, such as hormonal birth control, can help restore regular periods, keeping the uterine lining safe from developing endometrial cancer. This can also help improve PCOS-related acne and excess unwanted hair growth. Fertility treatments are available for women looking to get pregnant, allowing many women to conceive.
For more information or to make an appointment with the Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility service, call 1-833-UT-CARES (1-833-882-2737) or visit here.
